From Squiggly Words to Sliding Puzzles: The Ever-Evolving Saga of CAPTCHA
A journey through the evolution of CAPTCHA from distorted text to behavioral biometrics and the ongoing battle against bots.


The Beginning
Remember those days when signing up for an account involved deciphering a string of distorted letters and numbers? Yeah, those were the good old days (or not). That, my friend, was the OG CAPTCHA, standing for “Completely Automated Public Turing test to tell Computers and Humans Apart.” Basically, a digital bouncer trying to keep the robot riff-raff out of our online space.
The early CAPTCHAs, bless their hearts, were simple. Just some warped text that a human could (hopefully) read, but a computer couldn’t. It was a pretty decent strategy… for a while. With time the captcha’s kept becoming more distorted and harder to read, but like a wily villain in a superhero movie, bots started getting smarter. They evolved, learning to recognize even the most mangled text, making those original CAPTCHAs about as effective as a screen door on a submarine.
So, the CAPTCHA game had to level up. Enter CAPTCHA 2.0: the picture puzzle era. “Click all the squares with traffic lights,” they’d demand. Or, “Identify all the images containing a bus.” This felt more like a game than a security measure, and for a time, it worked! It required a bit more cognitive ability, something bots back then lacked.
Then came the age of the slider. “Drag the puzzle piece to complete the picture.” Smooth, intuitive, and arguably less annoying than its predecessors. Plus, it felt strangely satisfying to perfectly align that little puzzle piece. But, you guessed it, the bots eventually caught up. With advances in image recognition and machine learning, even these seemingly foolproof methods started to crumble.
And now? The landscape is shifting again. The rise of sophisticated AI models, like those powering image generation and even self-driving cars, has made traditional CAPTCHAs look like child’s play. These AI behemoths can often solve the most complex CAPTCHAs with alarming accuracy, leaving website owners scrambling for new ways to keep the bots at bay.
What can we do?
So, what can we do in this age of super-smart bots? The future of bot defense is moving towards more invisible methods. Things like analyzing user behavior, tracking mouse movements, and even looking at how long it takes someone to fill out a form. These subtle clues can help distinguish between a real human and a bot pretending to be one.
Here are some strategies which still works:
Behavioral Biometrics
Let’s dive deeper into the world of behavioral biometrics, one of the most promising frontiers in online security. Imagine a security system that doesn’t rely on what you know (passwords) or what you have (security tokens), but on how you interact with your device. That’s the essence of behavioral biometrics.
Instead of presenting explicit challenges like CAPTCHAs, behavioral biometrics works in the background, continuously monitoring and analyzing a user’s unique digital fingerprint. This fingerprint is composed of a multitude of subtle, subconscious behaviors that are difficult for bots to mimic. Think of it as a digital Sherlock Holmes, observing and deducing your identity based on your unique quirks and habits.
Here’s a breakdown of the key aspects that behavioral biometrics analyzes:
- Typing Dynamics: This looks at how you type, including your speed, rhythm, and the pressure you apply to keys. Do you frequently pause between certain letters? Do you tend to hold down keys slightly longer than average? These seemingly insignificant details contribute to your unique typing profile.
- Mouse Movements: The way you move your mouse cursor, including its speed, trajectory, and even how you hover over elements, can be surprisingly revealing. Do you move the cursor in straight lines or with slight curves? Do you hesitate before clicking a button? These subtle movements create a distinct pattern that’s difficult for bots to replicate accurately.
- Touchscreen Interactions: For mobile devices, behavioral biometrics can analyze how you interact with the touchscreen, including the pressure, angle, and speed of your swipes and taps. Each individual has a unique way of interacting with a touchscreen, and these nuances can be used to differentiate between a human and a bot.
- Device Orientation: How you hold your device, the angle of tilt, and how often you rotate it can also be incorporated into the behavioral profile. These subtle movements are often unconscious and difficult for bots to emulate consistently.
- Scrolling Patterns: The speed and rhythm with which you scroll through a webpage can also contribute to your behavioral fingerprint. Do you tend to scroll smoothly or in jerky movements? Do you frequently pause to read specific sections?
- Navigation Behavior: How you navigate through a website or app, including the order in which you click on links and the time spent on each page, can reveal valuable information about your browsing habits.
Advantages of Behavioral Biometrics:
- Passive and Seamless: Unlike CAPTCHAs, behavioral biometrics works behind the scenes, requiring no extra effort from the user. This creates a frictionless user experience.
- Enhanced Security: It’s incredibly difficult for bots to replicate the complex nuances of human behavior, making it a robust security measure.
- Continuous Authentication: Behavioral biometrics can continuously monitor user behavior throughout the session, providing an extra layer of security against session hijacking.
- Fraud Prevention: By identifying anomalies in user behavior, it can help detect and prevent fraudulent activities.
The Future of Behavioral Biometrics: As AI continues to advance, so too will the sophistication of behavioral biometrics. Future iterations may incorporate even more subtle cues, such as eye tracking and facial recognition, to create an even more comprehensive and accurate digital fingerprint. This technology holds immense potential to revolutionize online security, creating a safer and more seamless online experience for everyone.
While behavioral biometrics offers compelling security advantages, it also raises legitimate privacy concerns that need to be addressed transparently and proactively. Collecting and analyzing such granular data about user behavior inevitably raises questions about how this information is stored, used, and protected.
But (and it’s a big BUT) there is a huge privacy concerns associated with behavioral biometrics:
- Data Collection and Storage: The very nature of behavioral biometrics involves collecting a significant amount of personal data about how users interact with their devices. This data, while anonymized in some cases, can still be potentially sensitive.
- Data Usage and Purpose Limitation: Transparency about how the collected data is used is paramount. We need assurance that their behavioral data is being used solely for security purposes and not for other purposes, such as targeted advertising or profiling. Haha 😆 who I am kidding they will definitely use it to show us ads. Now I’m not against targeted ads, if I am gonna see ads then it’s better if it’s something useful for me. BUT the idea that a program knows me that much makes me feel really uncomfortable. If there’s a way that they don’t know me
- Profiling and Discrimination: There’s a risk that behavioral biometrics could be used to create profiles of individuals based on their online behavior. These profiles could potentially be used to discriminate against certain groups or individuals, leading to unfair or biased outcomes.
- Lack of User Control: As user we often have limited control over the collection and use of our behavioral data. We may not be aware of what data is being collected or how it’s being used. Just think that you laughed at a dark joke and next day you are in court 😝.
- Third-Party Sharing: Concerns arise when behavioral data is shared with third-party companies. Let’s say that you a trust company named A, and that company sold your data to a company B, B misused that data and now you are in trouble.
- Data Security Breaches: If a data breach occurs and behavioral data is compromised, it could have serious consequences for users. This data could be used to impersonate you or gain access to your accounts. They can use AI to create a clone of you then misuse it to extort your innocent loved ones.
- Cross-Device Tracking: Behavioral biometrics can potentially be used to track us across multiple devices, creating a more comprehensive profile of our online activities. This raises concerns about the potential for excessive surveillance and tracking.
What is the alternative then?
Honestly speaking, the perfect way does not exist you just have work arounds. The old image captcha with IP addresses you may be able to stop most of the botting attacks. To make sure that your captcha work against the AI you should simply accept simplicity over complexity. You can trick AI with decoy text which humans will ignore but bots will read. Just see this result from ChatGPT when I added decoy text over my captcha:
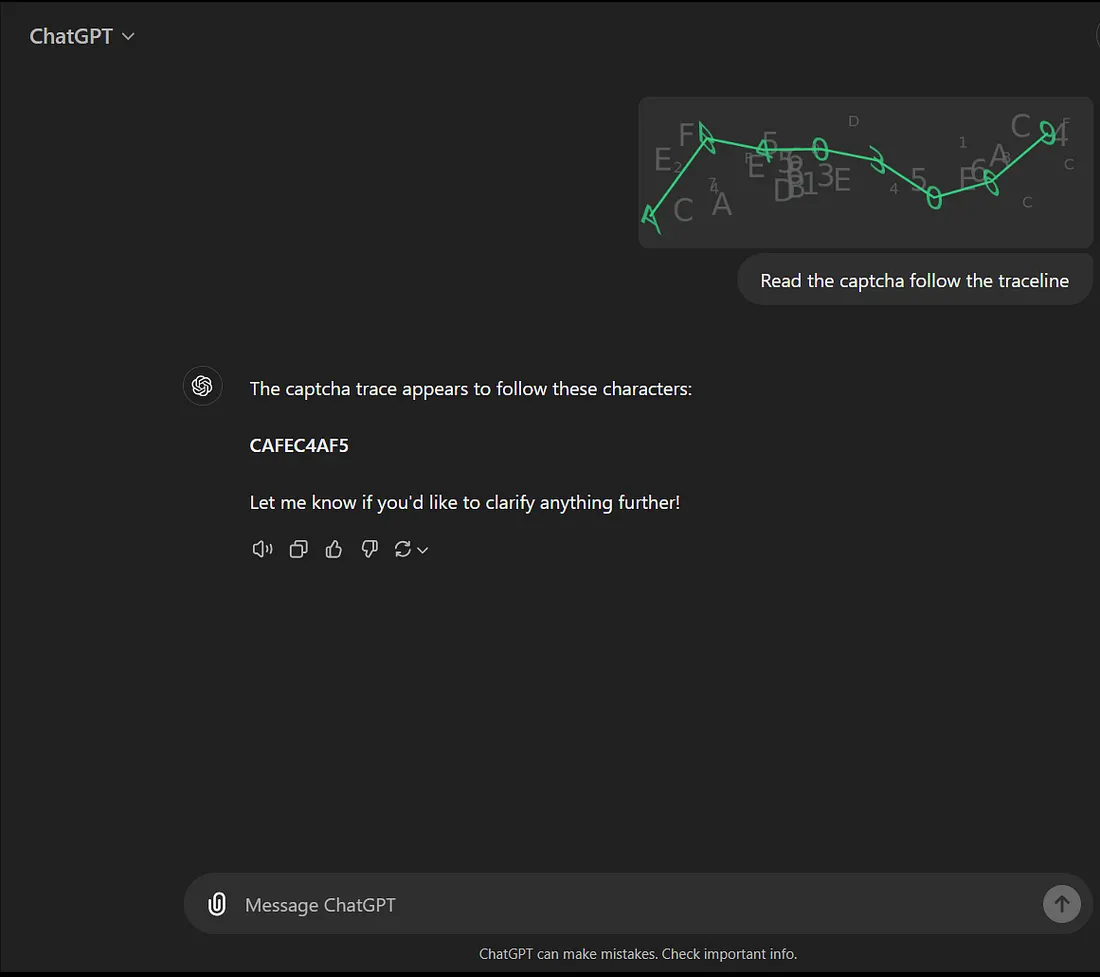
You can also try this with other ai models:

I have made a npm module which generates completely random captcha like above. Everything from trace line to captcha to decoy to background is customizable. You can check this here: Shashank3736/captcha-canvas: A captcha generator by using skia-canvas. (github.com)
Conclusion
The battle against bots is an ongoing arms race. As bots get smarter, our defenses need to evolve too. It’s a constant game of cat and mouse, but with the right tools and strategies, we can still keep our online spaces safe from the robotic hordes. So, the next time you encounter a CAPTCHA, take a moment to appreciate its humble beginnings and the ongoing struggle to keep the internet a human place and they are not invading your privacy to reduce there work 😸.
Related Posts
Gemini 2.5 Pro: Google's Most Advanced AI Model
An in-depth exploration of Google's Gemini 2.5 Pro - its thinking capabilities, advanced features, and position in the AI landscape.
- ai
- gemini
- llm
How ChatGPT saves GPU time? The Concept of Model Distillation
An in-depth exploration of LLM distillation - how large language models transfer knowledge to smaller, more efficient models for cost-effective AI deployment.
- llm
- ai
- chatgpt
- machine-learning
Building My Blog: Why I Chose Giscus for Comments
Why I integrated Giscus, a GitHub-powered open-source comment system, into my developer blog covering privacy, setup, pros, and tradeoffs.
- astro
- comments
- github
- open-source